Stem Cell Bra
TechnologyAN OVERVIEW OF THE STEMCELLBRA™ & ITS POTENTIAL TO AUGMENT BREAST SIZE
STEMCELLBRA™ TECHNOLOGY
SDF-1
StemCellBra™’s electrical stimulation mechanism instigates the over expression of SDF-1, known to be a homing signal for stem cells. SDF-1 has been proven to improve blood flow and tissue reconstruction in numerous studies in various models and tissues over the past decade without serious side effects reported.
The concept of the homing in the stem cell recruitment process is the most crucial step of stem cell transplantation1. It is the navigation process that enables stem cells from red bone marrow through the blood, the vessels, and to organs throughout the body, and in this case, breast tissue.
The Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy journal published an article on SDF-1’s capabilities in regenerative medicine. The study shows that SDF-1 plays a huge role in tissue engineering. They found that when tissue is injured, the organ in the injured area overly expresses SDF-1, therefore an elevated SDF-1 level results2. CD34+ progenitor cells, the cells found in red bone marrow that help create blood, are recruited and retained by SDF-1 to that injured site2.
VEGF
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) regulates the development of new blood vessels from existing blood vessels by inducing growth, movement, and permeability of blood vessel cells, hence the capability of the StemCellBra’s bioelectric stimulation mechanism to potentially cause increased blood flow to the breast tissue when therapy is administered3. Cell Transplantation journal presented a study that indicates in situ electrostimulation, through a cell and cytokine free stimulation system, enhanced heart muscle function and increased blood vessel development through the production of VEGF4. In situ electrostimulation is the face of the future in the repair of the heart and other organs; it also has the capability of preparing tissue for cell-based therapy treatment4.
StemCellBra™ has three products under development
BreastStim™
(lowest cost alternative)
Not FDA cleared yet – Investigational Use Only
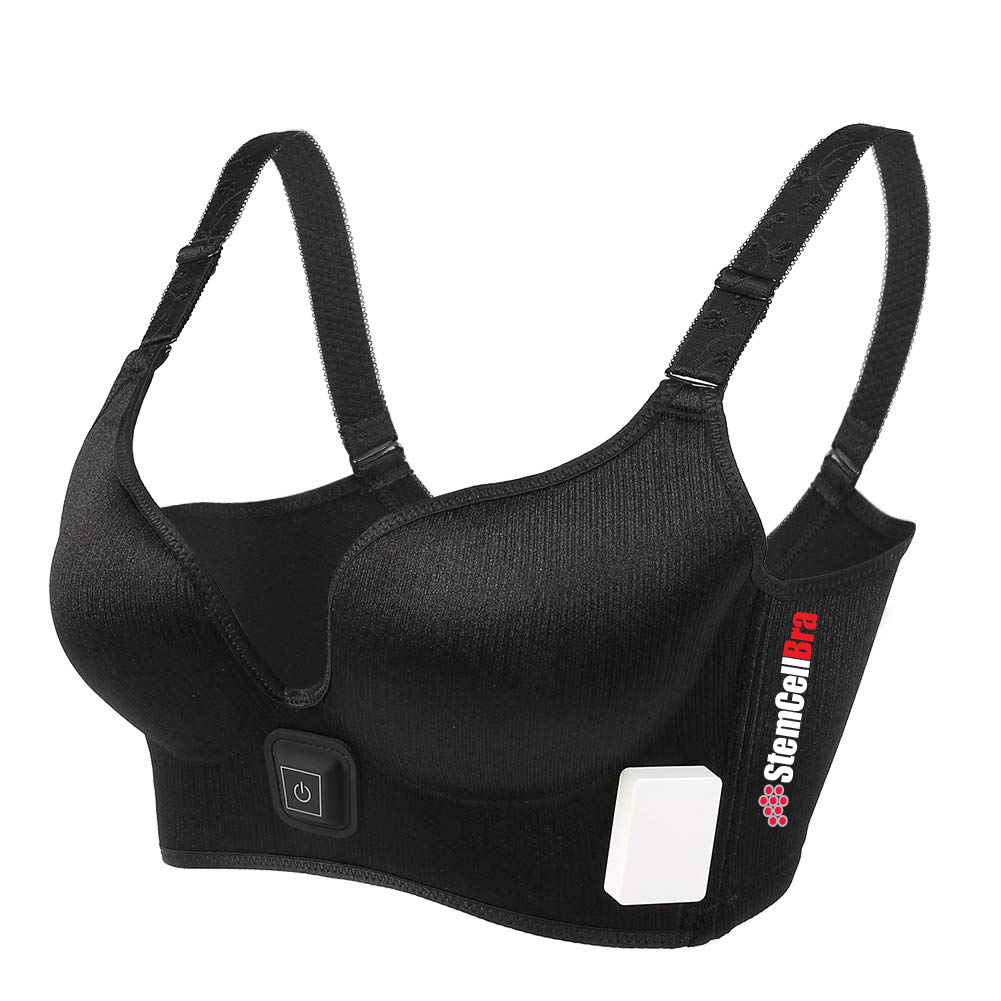

StemCellBra™
Wearable stem cell homing bra with shape forming mold with built-in micro stimulator wireless and proprietary high end gold-carbon polymer conductive gel electrode inserts
Not FDA cleared yet – pre-clinical development

StemCellBra Plus™
Bioelectric stimulation stem cell homing bra combined with fat grafting and supplemental injections of the SC-15 breast tissue generation mixed composition which includes PRF
and adipose tissue stromal fraction
Not FDA cleared yet – Investigational
Bedside adipose tissue processor

BioPRF
For more information click here bio-prf.com

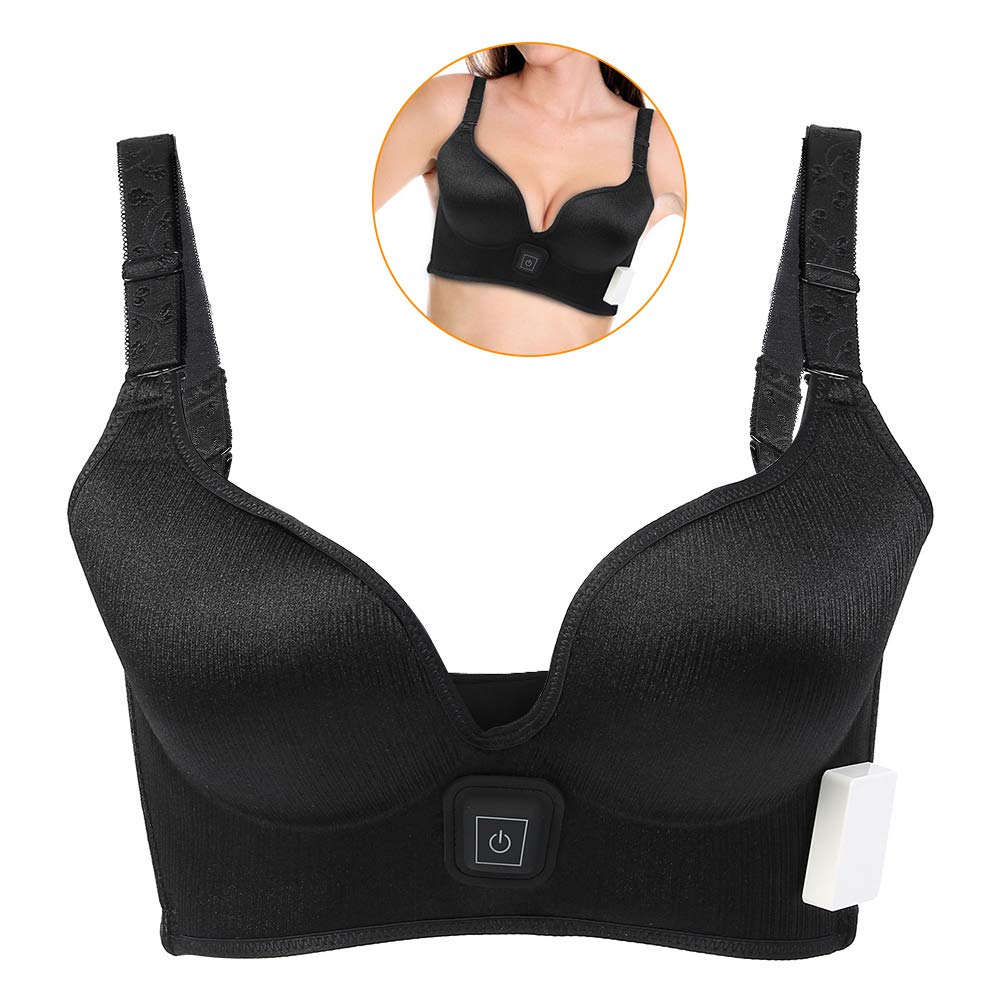
Connected
StemCellBra™ connected by wire to stimulator and portable device design battery pack.
The stimulator is to be worn on the belt line, hidden under clothes (comparable to people that are wired for microphones for TV)

Portable Device
StemCellBra™ utilizes a portable device design

Conductive Electrode
StemCellBra™ conductive electrode gel pad design and battery pack



INITIAL PRE-CLINICAL TRIAL METHODOLOGIES & RESULTS
This was an ovine breast electrical stimulation pilot trial conducted in Buenos Aires, Argentina, supervised by Dr. Jorge Genovese, one of the founding members of Leonhardt’s innovation accelerator. The following factors were assessed in the trial: how the electrical stimulation effected potential growth of breast tissue, ovine breast tissue tolerance of the electrical stimulation, and monitoring mammary tissue histological changes, with a focus on new blood vessel development and stem cell populations5.
Three Romney marsh female sheep were involved in the study. The sheep had never given birth, were in reproductive age, and presented with an average weight of around 85 pounds5.
Three veterinarians were involved in the workflow of the study. One of the veterinarians assessed how the sheep’s external mammary glands tolerated the treatment. Another veterinarian was responsible for initial and final echo evaluation. A third veterinarian took the biopsy specimens’ collection. Out of these three veterinarians, the latter two veterinarians had no knowledge of the sheeps’ roles in the trial. In addition, the pathologist was also unaware of the sheeps’ roles in the trial5.
Every other day for 30 days, the StemCellBra™ self-adhesive electrodes were placed on the sheep mammary glands for 60 minutes in the following stimuli intervals: 250 uA, 100 Hz, and bipolar. At Day 0 and Day 30, an ultrasound exam was administered to the dorso-ventral aspect, latero-medial aspect and the volume of the mammary glands5.
The descriptions below reflect how each sheep was treated:
• SHEEP I: Control
o The electrodes were attached BUT not connected.
• SHEEP II: Both breasts were treated
• SHEEP III: ONLY the right breast was treated
• GOAT Anti-mouse IgG H8L (FITC) pre-absorber AB7064
• Anti CD105 Antibody (8A1) AB156756
• AntiCD34 Antibody (EP373Y) AB81289
During the study, the sheep showed no signs of pain or discomfort. Any other local or systemic adverse reactions were detected. The sheeps’ photoperiod in the season the study was conducted may have been a major influence in some of the treated sheeps’ mammary gland size reduction.
This photoperiod is critical in ovine and determines changes in their sexual organs. In the sheep where only one mammary gland was treated, this aspect is a key in the evaluation of the results. While the treated side experienced a minor increase in size, the sheep seemed to be in a clear regressive mammary period based off the changed in the untreated side5.
Connective tissue proliferation without retracted areas was noted in the histology findings. Laxity abundance was also noted based on a reduced stromal cell population. Ductus and vessel increase at the parenchyma was present as well. CD34+ cells that in the control were around the in the control tissue, some vessels had CD34+ cells. In the treated tissue, these same cells were also detected in limited numbers. These findings were based on limitations due to restrictive access to specific reactives. In the treated glands, CD105+ were detected in the parenchyma. Inflammation nor other pathological conditions were noted5.
Stem Cell Bra’s designed mechanisms of action are multi-fold:
1
The electrical signal causes cells in the breast tissue to release the SDF-1 protein which is a homing signal which causes stem cells coming from bone marrow, fat tissue and circulating blood to come to the breasts.
2
Once a bolus of stem cells have been recruited the electrical signal changes to the proliferation mode and causes the recruited stem cells to multiply which further enhances breast volume.
3
The third signal causes new blood vessels to grow to ensure the newly created breast tissue is well fed to maintain survival.
The stem cell bra patent application serial no. 61/749,642 APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR INCREASING BREAST SIZE filed January 7, 2013 with USPTO Inventor: Howard J. Leonhardt, Santa Monica, California
This application is a coupled to previous already U.S. patented Leonhardt et al inventions utilizing electrical stimulation to recruit stem cells, proliferate them (including resident cells) and differentiate them into selected tissues.

